Fast forward to more info on
- Open the 50five-app.
- Select 'Support'.
- There are 3 options:
1. Via the chatbot
- 'Chat with the AI agent’ is coming soon
2. Via the Frequently asked questions
- Scroll to Frequently asked questions
- Click on the desired question
3. Via the contact page
- Scroll all the way down and select 'Visit contact page'.
- You will be redirected to an external website. Click on 'Open'.
- Scroll down to 'Contact form our customer support'
- Choose a category for your ticket.
- Carefully fill in all the requested details; use your professional e-mail address.
- Click on ‘Send’.
Please note: these tickets will not be logged in the 50five-app.
- Open the 50five app and select ‘Support’.
- Scroll all the way down and select 'Visit contact page'.
- You will be redirected to an external website. Click on 'Open'.
- Scroll down to 'Contact form our customer support'.
- Choose a category for your ticket.
- Fill in all requested details carefully, using your professional e-mail address.
- Click on ‘Send’.
Please note: these tickets are not logged in the 50five-app.
It takes 10 minutes tops to fill up a diesel or petrol car and you’re good to go for another 600 to 900 km, whereas it takes 10 hours to charge an electric vehicle with a driving range of 400 km – that’s quite a difference!
How can I find out if I qualify for an electric driving profile?
You qualify for an electric driving profile if you fully agree with the following three statements:
1. My electric vehicle’s driving range is more than sufficient for my day-to-day drives
2. I can charge my electric vehicle safely and efficiently, so I can always start my next drive with peace of mind
3. I can find an electric vehicle that checks all my boxes and is within my budget.
One of the key aspects of electric vehicles is often their driving range; i.e. the distance you can drive with a fully charged battery without having to stop to charge your vehicle.
Together with the charging solution and the available budget, the range is one of the determining factors in the choice of electric vehicle.
The range of your electric vehicle, depends on
- The usable energy capacity of the battery (in kWh)
- The actual consumption in (in kWh per 100 km), which depends to a large extent on driving style and driving conditions (for example, whether you have the heating or air conditioning on)
Table: the driving range depends on the usable battery capacity and the actual consumption
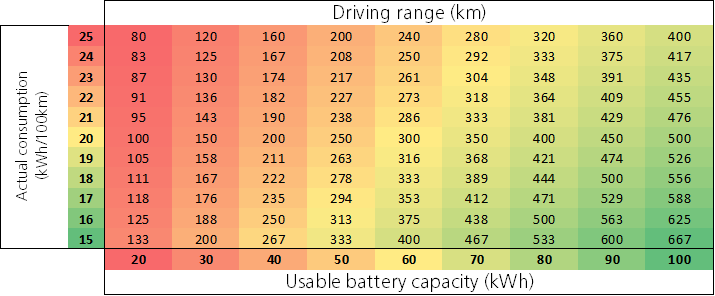
Use the following rule of thumb when choosing your electric vehicle: driving range ≥ daily kilometres × 1,5
This way, your driving range will be sufficient for your day-to-day drives without you having to stop to charge your vehicle, even in winter when the heating is on or in summer when the ai conditioning is on.
- If you drive 80 km every day, the range must be at least 120 km
- If you drive 200 km every day, the range must be at least 300 km
Short-range electric vehicles are the best driving solution for urban environments, while long-range electric vehicles are perfect for longer motorway journeys, making them a viable alternative to petrol and diesel cars, even if you drive 50,000 km or more a year.
When you drive an electric vehicle, you want to be able to charge your vehicle safely and efficiently, so you can always start your next drive with peace of mind.
The perfect solution: a home charging station
A home charging station offers a number of benefits, such as charging at reasonable kWh rates, and being able to let your housemates, visitors and even your neighbours use it, whether in return for payment or free of charge.
If you are the tenant of a house or apartment, you will need to make clear agreements with the owner.
If you are the owner of a house or apartment, you will need to make clear agreements with the trustee.
Charging your vehicle at work and/or at public charge points
If your home is not suitable for the installation of a charging station, we recommend spending some time researching your options for charging your vehicle at work and/or at public charge points.
If that all checks out and there are sufficient alternative charging options available, go for it!
Be sure to factor in your day-to-day drives, battery capacity and actual consumption when choosing your electric vehicle.
Are there no or insufficient charging options available?
Or exceeds the cost of an electric vehicle your budget?
We recommend choosing a fuel-efficient fossil-fuel vehicle.
The third and final aspect – leasing budget – is where employee and employer both come into play. Your employer sets the budget, subject to a certain limit, which you can use to select a vehicle.
Check the rules on budget allocation in your employer’s car policy (fleet regulations) and/or in KBC Movesmart.
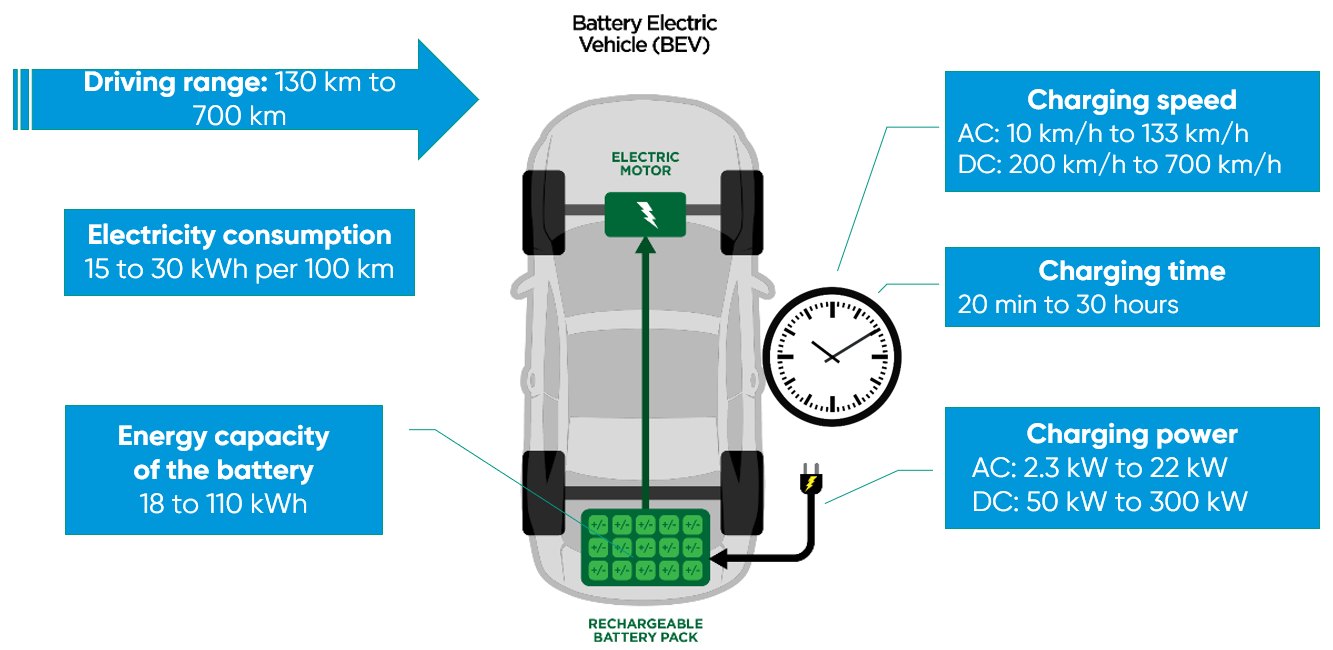
The concept of electric vehicles is actually fairly straightforward. We connect a battery to an electric motor, add four tyres and now we have an electric vehicle.
Electric motor
Electric vehicles are powered by one or more electric motors.
Electric motors are powered by electric energy supplied by the battery.
Battery
Electric vehicles are equipped with a battery which supplies and receives direct current, whereas the public electricity network uses alternating current. To be able to charge the battery of an electric vehicle off the grid, every electric vehicle is equipped with a converter, which converts alternating current into direct current.
Battery capacity
The energy is stored in the battery. The battery’s energy capacity (or battery capacity) is expressed in kilowatt-hour (kWh) and ranges from 15 kWh to over 100 kWh.
Consumption
An electric vehicle’s consumption is expressed in kWh per 100 km and ranges from
10 to 25 kWh per 100 km
Driving range
The average range of a fully charged battery is between 100 and 500 km, depending on the battery’s energy capacity and on consumption.
Combustion engines and electric motors
A plug-in hybrid vehicle has two engines: an internal combustion engine (generally petrol-driven) and a powerful electric motor.
A PHEV is very powerful because the internal combustion engine and electric motor can also operate simultaneously.
The vehicle has a low official fuel consumption (theoretically) and therefore also low CO2 emissions.
Battery
The battery can be charged in advance from the mains or at a charging station.
Battery capacity
Up to 34 kWh
Driving range
Depending on the vehicle, up to 140 km can be driven entirely on electric power. Once the battery is empty, the petrol or diesel engine takes over.
To see which makes and models are available, browse the various car manufacturers’ websites
or check out the comprehensive database at https://ev-database.uk .
While you don’t need to be a tech expert to drive an electric vehicle and know how to charge it, it does help to know your way around some of the terminology.
One of the key aspects of electric vehicles is often their driving range, i.e. the distance you can drive with a fully charged battery without having to stop to charge your vehicle.
As with fossil-fuel vehicles, the driving range of electric vehicles depends on two parameters:
- The amount of energy stored in the battery pack or fuel tank
- Actual consumption
If you know how full your battery is and how much energy the vehicle consumes, it is easy to calculate the actual driving range:
usable battery capacity / actual consumption = actual driving range
Charging power is an important factor when it comes to electric vehicle charging. The higher the charging power, the faster the charging speed.
The following factors determine how long it takes to charge an electric vehicle at a charging station
- The battery charger/converter in the vehicle
- How many phases can the converter process?
- What is the maximum amount of current (in amperes) that the converter can supply?
- The charging station connection (number of phases and amperes) to the electricity grid
- The electrical home installation (number of phases and amperes)
The maximum power for charging an electric vehicle depends on the weakest link in the chain (in other words, you can only charge as fast as the weakest component allows).
Charging power is expressed in kilowatts or kW for short. 1 kilowatt = 1,000 watts.
Energy is power during a certain period of time and is expressed in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
The energy capacity of an electric vehicle’s battery is expressed in kWh.
The battery capacity of today’s electric vehicles is between 15 and 100 kWh.
Example: the range of an electric vehicle with a real battery capacity of 60 kWh and an actual consumption of 15 kWh per 100 km is 400 km.
As with fossil-fuel vehicles, an electric vehicle’s consumption is expressed in ‘amount of fuel’ per 100 km, but instead of ‘litres’, the term used for electric vehicles is ‘kilowatt-hours’ (or kWh for short).
The average consumption of today’s electric vehicles is between 15 and 30 kWh per 100 km.
The charging time is the number of hours and/or minutes it takes to charge the electric vehicle’s battery from 0% to 100%.
The charging time depends on
- The battery’s energy capacity (in kWh)
- The maximum charging power (in kW)
How is the charging time calculated for fully charging an empty battery
(linear calculation)?
battery's energy capacity in kWh / (charging power in kW × efficiency of 90%)
Example
- 64 kWh / (2,3 kW x 90%) = 31 h
- 64 kWh / (7,4 kW x 90%) = 9 h 30 min
The charging speed represents the number of kilometres of range added to the battery’s capacity per hour charged.
The charging speed depends on
- The maximum charging power (in kW)
- The electric vehicle’s energy consumption (in kWh per 100 km)
How is the charging speed calculated?
(charging power in kW ×efficiency of 90%)/(consumption in kWh per 100 km)
Example
- (2.3 kW x 90%) / 15 kWh per 100 km = 14 km/h of 7 h 15 min. per 100 km
- (7.4 kW x 90%) / 15 kWh per 100 km = 44 km/h of 2 h 15 min. per 100 km
No car can run without energy. Conventional cars get their energy from petrol or diesel, while electric vehicles get theirs from the battery. And the battery is charged off the grid.
There are three charging methods – or modes – for electric vehicle batteries.
| Charging method | AC or DC* | Electric Energy Source | Number of phases | Charging cable |
| Mode 2 | AC charging | Regular socket | Single-phase | Secured |
| Mode 3 | AC charging | Charging station | Single-phase or three-phase | Secured |
| Mode 4 | DC charging | Fast-charging station | Three-phase |
Secured |
*AC charging = charging with alternating current
DC charging = charging with direct current
Mode 2 – AC charging means charging using a standard household socket via a separate charging cable with built-in protection.
- Mode 2 – charging cables
- The charging cable supplied with the vehicle
- A smart charging cable
- Maximum charging power = 2,300 W or 2.3 kW
- Charging time* for a range of 100 km = 7 h 15 min
- Charging speed* = 14 km/h
* based on electricity consumption of 15 kWh per 100 km
Important note: Never use an extension cord.
Mode 3 – AC charging means charging at a charging station that is integrated into the electrical home installation.
Mode 3 is used by public and semi-public charge points, home charging stations and charging stations at your workplace.
- Charging power between 3.7 kW and 22 kW
- Charging time* for a range of 100 km = between 45 min. and 4.5 hours
- Charging speed* from 22 km/h to 133 km/h
* based on electricity consumption of 15 kWh per 100 km
Tip
Always keep two charging cables in the boot of your electric vehicle:
- A Mode 3 charging cable for use at a (public) charging station
- A Mode 2 charging cable (with built-in protection) for charging using household sockets
The Type 2 sockets at a charging station and on an EV are not identical but complementary. As a result, the charging cable can only be connected on one end, even if both ends are Type 2.
Certain electric vehicles are designed for three-phase charging. To be able to charge an electric vehicle at home
- You must have a three-phase connection to the grid
- Your home charging station needs to have a three-phase connection
- You need to use a proper charging cable
Three-phase charging requires a 400 V supply. A transformer is required for a 230 V three-phase connection to enable three-phase charging (some electric vehicles can be charged using a three-phase charging station supplied with 230V, but then only two out of three phases will be used, resulting in lower power).
Whether you have a three-phase 3 x 230 V or 3 x 400 V+N is not an option you can personally select, as it depends on the electricity network in your street.

For instance, based on an electric vehicle with a battery capacity of 64 kWh and
an electricity consumption of 15 kWh per 100 km
| Charging power 1 | Charging time2 | Charging speed3 |
| 3,7 kW | 19h 15 min. | 22 km/h |
| 5,8 kW | 12h 15 min. | 35 km/h |
| 7,4 kW | 9h 30 min. | 44 km/h |
| 11,1 kW | 6h 25 min. | 66 km/h |
| 17,3 kW | 4h 05 min. | 103 km/h |
| 22,2 kW | 3h 15 min. | 133 km/h |
1 Provision: the charging station and electric vehicle must be maximally aligned based on
- The number of phases of the electric vehicle’s converter
- The amount of current that the converter can supply
2 Time required to fully charge an empty 64 kWh battery (linear calculation)
3 Charging speed based on electricity consumption of 15 kWh per 100 km

Mode 4 – DC charging means charging at a fast-charging station with direct current, in which case the battery is charged directly by the charging station, enabling significantly higher charging speeds than with alternating current; To be able to charge at a fast-charging station, the electric vehicle must be suitable for this purpose.
- Charging power between 50 kW and +175 kW
- Charging time* for a range of 100 km = between 6 and 20 min.
- Charging speed* from 300 km/h to + 1 000 km/h
* based on consumption of 15 kWh per 100 km and on the vehicle’s converter
The charging cable at fast-charging stations is always permanently connected to the charging station. Many fast charging stations are equipped with three cables, each with a different EV connector:
- CCS (Combined Charging System) for fast charging in Mode 4
- CHAdeMO (Charge de Move) for fast charging in Mode 4
- Type 2 for charging in mode 3
There are three determining factors for the maximum power when charging an electric vehicle at a charging station.
- The connection of the electrical installation to the electricity grid
- Single-phase or three-phase?
- 1 x 230 V, 3 x 230 V or 3 x 400 V? If three-phase, is there a neutral conductor (N)?
- The connection of the charging station to the electrical installation
- Single-phase or three-phase?
- What is the current (in amperes) per phase?
- The on-board charger or converter in the electric vehicle
- How many phases can the vehicle’s converter process?
- What is the maximum amount of current (in amperes) that the vehicle’s converter can supply?
The weakest link in the chain determines the maximum charging power (in other words, you can only charge as fast as the weakest component allows).

Example 1: You have an electric vehicle with a 25A single-phase converter
- Which connection provides the highest charging power?
- A single-phase connection of at least 25A
- The maximum charging power = 5.8 kW
- What if the charging station has a 32A single-phase connection?
- The electric vehicle’s converter can only handle 25A
- The maximum charging power = 5.8 kW
- What if the charging station has a 16A three-phase connection?
- The electric vehicle’s converter can only handle single-phase charging
- The charging station can only supply 16A per phase
- The maximum charging power = 3.7 kW
Example 2: You have an electric vehicle with a 32A three-phase converter
- Which connection provides the highest charging power?
- A 32A three-phase connection
- The maximum charging power = 22.2 kW
- What if the charging station has a 16A three-phase connection?
- The charging station can only supply 16A per phase
- The maximum charging power = 11.1 kW
- What if the charging station has a 25A single-phase connection?
- The charging station is suitable for single-phase charging only
- That single phase is suitable for 25A only
- The maximum charging power = 5.8 kW
| Electric energy source | Maximum charging power* | Charging speed (based on consumption) |
Charging time for a range of 100 km of 15 kWh per 100 km) |
| Socket (mode 2) | 2.3 kW | 14 km/h | 7 h 15 min. |
| Home or public charging station (mode 3) | 3.7 kW | 22 km/h | 4 h 30 min. |
| 5.8 kW | 35 km/h | 2 h 50 min. | |
| 7.4 kW | 44 km/h | 2 h 15 min. | |
| 11.1 kW | 66 km/h | 1 h 30 min. | |
| 17.3 kW | 103 km/h | 1 h | |
| 22.2 kW | 133 km/h | 45 min. | |
| Fast-charging station (mode 4) | 50 kW | 300 km/h | 20 min. |
| 175 kW | 1 000 km/h | 6 min. |
* At a consumption of 15 kWh per 100 km
As a tenant, you do not have the right to have a charging station installed at your own initiative. Such decisions are up to the owner.
If you do have a charging station installed, it becomes the property of the owner of the house or apartment you’re renting, even if you paid for it.
If you cannot have a home charging station installed, you will have to charge your vehicle at public charging stations or at work.
- To charge your EV at public charging stations, you need a charge card, such as the NFC charge card, which you can use to charge your vehicle at more than 99% of public charging stations in Belgium.
- Your employer’s car policy should stipulate whether you can charge your vehicle at work.
Make sure to carefully plan your charging sessions at work or nearby, especially if you’re planning a longer drive.
Take the test with the ‘Guide to Driving Electric Vehicles’ (only in Dutch). In a few steps, you will find out whether electric driving is the right choice for you and which electric vehicle is the best fit for you.
Since not every home or apartment is suitable for the installation of a charging station, and in some cases it can take up to several months to have the charging infrastructure set up, it’s best to start making the necessary arrangements as soon as possible!
- If you live in Flanders, you will find detailed information and a brochure on the Fluvius website
- If you live in Wallonia, there are several network operators to choose from: ORE, Resa, AIESH, REW. See the ORES website for more details.
- If you live in Brussels, you will find more information on the Sibelga website.
Tenants
If you rent an apartment, contact the owner to discuss the possibilities.
Lease car drivers
If you drive a lease car, check your employer’s car policy. A lot of employers offer the option to include a home charging station in your lease contract. Your charging station will then be connected to your individual electricity meter and you will pay the additional costs for installing the charging station (in addition to the price you pay under your lease contract) and infrastructure changes yourself.
More information on leasing an electric vehicle with a charging station is provided at this link.
You can use your charge card provided the charging solution meets a number of conditions:
- The charging station must be equipped with a module that allows ‘guest usage’.
- The charging station must have a card reader to swipe your charge card to start a charging session.
- The charging station must be equipped with RFID technology to enable data exchange between the charging station and the charge card provider. RFID is an acronym for Radio Frequency Identification.
Charging costs are billed through the charge card provider.
Yes, though this will be at your own expense.
Any request to relocate a charge point must be submitted through KBC Autolease and carried out by an installer approved by 50five.
KBC Autolease must submit two requests to %%brand.autolease.chargingsolution%%:
- Disassembly of the charge point at the current address (the device itself remains on-site). Disassembly and reassembly are not always carried out by the same installer or on the same date. This means you have to take the charge point to the new address yourself.
- Installation of the charge point at the new address – you will be contacted by 50five via video call to discuss the best charging solution.
Please bear in mind that costs include:
- Dismantling the charge point (202 euros)
- Installing the charge point at your new home (you will receive a quote)
- AREI inspection
These costs will be invoiced to the driver or customer.
In combination with an electric vehicle, KBC Autolease offers three charging solutions in the lease contract:
- A comprehensive charging solution in the initial lease:This includes a home charge point, a subscription to the charge point and a charge card.
- A comprehensive charging solution in the subsequent lease:A subscription to the charge point from a previous KBC Autolease lease and a charge card.
- A charge card only
More info on charging solutions and prices
KBC Autolease has partnered with 50five for charge points and Shell Fleet Solutions for charge cards.
50five is a Charge Point Operator (CPO)
The Charge Point Operator (CPO) is the party responsible for the management and operation of the charge point for the owner. The CPO monitors and manages the charge point transaction data, based on which it can offer a number of smart services. The owner of the charge point can use the CPO’s platform to determine whether the charging facility is private or public. The CPO can reimburse the consumer/employee for the home charging sessions and invoice the employer (through the leasing company if applicable).
Shell Fleets Solutions is a Mobility Service Provider (MSP)
The Mobility Service Provider (MSP) is the charge card issuer. The charge card is used to start and end a charging session and also determines the billing process. If the charge card is used at a public or semi-public charging station, the MSP determines the amount ultimately billed to the end customer based on the applicable roaming contract.
For KBC Autolease's comprehensive charging solution – a charge point, a subscription to the charge point and a charge card – Shell Fleet Solutions is the MSP for the charge card (Network Fleet Card).
The comprehensive KBC Autolease home charging solution comprises:
- a 50five charge point (including installation and AREI inspection)
- a subscription for the charge point (including reimbursement of home charging sessions)
- a charge card – Shell’s hybrid Network Fleet Card – for electric charging at your home charge point and at over 99% of public charging stations in Belgium
50five is the charge point operator (CPO) and Shell is the charge card issuer (MSP). The charge card is linked to the charge point by 50five and registered as a ‘known’ charge card.
This offers the following benefits:
- The reimbursement rate (in euro per kWh) is automatically set by 50five at the CREG rate and is charged directly to the employer without VAT or additional roaming charges.
- Given that VAT does not apply to advanced charges (Art. 28, 5° of the VAT Code), the billing of home charging sessions is likewise free from VAT.In practice, the cost of home charging sessions is advanced by KBC Autolease in the name and for the account of the company and then recovered at a later date.
Important: KBC Autolease can only register a charging session as being a home charging session if 50five is the operator of the charge point and Shell is the issuer of the charge card. In addition, the charge point must be included in a current or previous lease with KBC Autolease and the charge card must be included in the current lease.
When you drive an electric vehicle, you want to be able to charge your vehicle safely and efficiently, which is why we highly recommend a home charging station. Using a home charging station has a number of advantages.
- Your vehicle charges much more quickly than when you simply plug it into a mains socket
- Charging stations deliver more power than a mains socket
- Electricity at home is cheaper than at a public charging station
- The electricity consumption is measured and can be set off
- There is no risk of overheating with a charging station
You can have a charging station installed in your garage, on your driveway or under your carport. You will need to ensure you have enough space for it. The garage can be adjacent to your home, but it can also be a separate or free-standing garage or an underground garage.
If 50five is not the operator (CPO) of the home charge point, the installation of the charge point and reimbursement of home charging sessions would be carried out by another party.
If your KBC Autolease lease includes a charge card and you want to use it to charge up at your own charge point, you should consider the following when choosing your charge point:
- In order for home charging sessions to be reimbursed to the employee and billed to the employer, the charge point must be connected to the CPO’s back-office system.
- In most cases, the CPO’s back-office system will not permit a Shell charge card to be registered; in such cases, charges will be settled based on the applicable roaming rates agreed between Shell – as the charge card issuer – and the CPO.In this scenario, the charge point must be semi-public so as to allow guest usage.
Important: KBC Autolease can only register a charging session as being a home charging session if 50five is the operator of the charge point and Shell is the issuer of the charge card. In addition, the charge point must be included in a current or previous lease with KBC Autolease and the charge card must be included in the current lease.
This is because Shell cannot distinguish another operator’s charge point from a public charging station. These charging sessions are subject to 21% VAT.

KBC Autolease offers Shell's hybrid Network Fleet Card.
You can use the national ‘hybrid’ charge card in Belgium
- for electric charging
- at your home charge point
- at work, if possible
- at 99% of public charging stations (AC chargers) and fast chargers (DC chargers) such as Ionity and Fastned, excluding Tesla Superchargers Use the Shell Recharge app to find available public charge points near you and on the road
- for filling up with fossil fuel
If you opt for the international ‘hybrid’ charge card, you also have access to the Shell Recharge Solutions network, the largest network of public charging stations with 700 000 charge points across 35 European countries, and you can refuel at all Shell filling stations and most Esso, Eni and Avia filling stations throughout Europe.
The Shell Recharge app lets you find available public charging stations near and on the road.
More info on charge cards
If your KBC Autolease lease includes a charge point, charge point subscription and charge card, and if your employer reimburses home charging sessions, it is possible to set up automatic reimbursement. The standard reimbursement rate (in euros per kWh) is based on the regional CREG rate.
- The CREG rate is set automatically by 50five
- The charge point records how much electricity is consumed at your home (expressed in kWh) and sends this information to 50five
- The driver will receive:
- a monthly reimbursement document from 50five (delivered around the 15th of each month) detailing the previous month’s home charging sessions
- monthly reimbursement of their home charging sessions from Threeforce B.V. based on how much they consume and the CREG rate set. The first payment is made around six weeks after sending the reimbursement document, the following payments are made after four weeks. Example: for charging sessions in May, you will receive the reimbursement document around 15 June and the amount being reimbursed will be paid into your account around 15 July.
- These charging sessions are invoiced to KBC Autolease
- KBC Autolease sends an invoice for a monthly advance electricity charge to your employer and the actual costs are then settled on a periodic basis.
What you have to do:
- link your KBC Autolease charge card to your 50five charge point and then set up automatic reimbursement
Use the free Shell app to find available public charge points in your area and on the road.

You can download the app by scanning this QR code.
- KBC Autolease’s quote covers both the electric vehicle and the charging solution.
- Electric vehicle
- Financial lease
- Complete service package (repairs, maintenance, tyres, insurance, etc.)
- One of three charging solutions
- A comprehensive charging solution in the initial lease:
This includes a charge point, a subscription to the charge point and a charge card. - A comprehensive charging solution in the subsequent lease:
A subscription to the charge point from a previous KBC Autolease lease and a charge card. - A charge card only
- A comprehensive charging solution in the initial lease:
- Open KBC MoveSmart
Learn more about KBC MoveSmart
- Go to ‘Quotes’ and select (‘Car Quote’) to costbegin your simulation
- Select your mobility plan
- Customise your electric vehicle (packs, options and any accessories) using the codes on your dealer quote where possible
- Choose your charging solution.
- I want a charge station, including a subscription and charge card
- I want a new charge card and a new subscription for my charging station from a previous KBC Autolease contract
- I only want a charge card to charge at public charging stations
- I will arrange everything myself. I don't want a charging station or charge card from KBC Autolease
- Choose the colour and upholstery you'd like
- Check the vehicle price and selected options in the summary
- Save your quote by selecting ‘Save’
- If you're ready to order, select 'Approve'. KBC Autolease will order your electric vehicle and, if necessary, inform 50five of your charge point order.
Ask KBC Autolease for a quote that covers an electric vehicle and your preferred charging solution.
- KBC Autolease
- orders your electric vehicle from the selected dealer
- notifies 50five of your charge point order
- 50five
- will call you to schedule a video appointment
- will take the necessary photos during the appointment, offer advice on the best location for the charging solution and inform you whether there are any additional installation costs on top of the price of the basic installation (e.g., for excavation work or mounting the charge point on a pole)If it is not possible to make an accurate assessment during the video appointment, a specialist from 50five will perform an on-site inspection (this costs 202 euros excluding VAT)
- KBC Autolease receives the quote from 50five for the standard installation and immediately approves it.
- 50five’s quote for any additional installation costs is sent to the driver, who must then approve it to proceed.
- 50five will call you to schedule the installation. Installation takes place about six weeks after the quote is approved. The installation is subject to inspection: 50five schedules the appointment with an AREI inspector.
- An AREI inspector inspects the installation. Upon approval, you may charge your electric vehicle at your charge point.
- KBC Autoleaseo notifies you when your electric vehicle is ready for delivery at the dealershipo gives approval to 50five to activate your charge point and link it to KBC Autolease's charge card
- 50five activates your charge point: you can now charge your vehicle with your charge card at your own charge point (your charge card was already activated for use at public charging stations). Your charge card is included with your vehicle’s documents or it will be sent to you.
- LastMileSolutions will send you an e-mail to register on their platform and/or log in to the 50five app.
- You make an appointment with the dealership to collect your electric vehicle.
That’s it! You can now drive with peace of mind and charge your vehicle anywhere.
A preliminary investigation is indeed necessary. On the one hand, to make sure that a charging station can be safely connected to the current electricity installation. In addition, it is also the only way to provide an accurate quote for the end user's specific home situation.
This investigation is carried out by 50five via a video call. During this video call, the 50five employee takes the necessary photos and advises you on the best location for the charging solution and on any additional installation costs. These are additional installation costs that exceed the price of the basic installation, for example excavation work or mounting the charging station on a pole.
No.
KBC Autolease will only request an inspection from 50five after receiving a signed lease quote.
As soon as the vehicle is ready for delivery, KBC Autolease will inform you and notify 50five that your charging station may be activated.
50five will send you (via LastMileSolutions) an e-mail with clear instructions on how to register on their platform, log into the 50five app and link your charging card, among other things.
You link your charge card (delivered by KBC Autolease) to your account. From now on, you can charge with your charge card at your own charging station. The charging card is already activated anyway for use at public charging stations.
If your KBC Autolease lease includes a charge point, charge point subscription and charge card, and if your employer reimburses home charging sessions, it is possible to set up automatic reimbursement. The standard reimbursement rate (in euros per kWh) is based on the regional CREG rate and is set by 50five.
- The charge point records how much electricity is consumed at your home (expressed in kWh) and sends this information to 50five
- The driver will receive:
- a monthly reimbursement document from 50five (delivered around the 15th of each month) detailing the previous month’s home charging sessions
- monthly reimbursement of their home charging sessions from Threeforce B.V. based on how much they consume and the CREG rate set. The first payment is made around six weeks after sending the reimbursement document, the following payments are made after four weeks. Example: for charging sessions in May, you will receive the reimbursement document around 15 June and the amount being reimbursed will be paid into your account around 15 July.
- These charging sessions are invoiced to KBC Autolease
- KBC Autolease sends an invoice for a monthly advance electricity charge to your employer and the actual costs are then settled on a periodic basis.
What you have to do:
- link your KBC Autolease charge card to your 50five charge point and then set up automatic reimbursement
- You should have received a Network Fleet Card for charging when your vehicle was delivered (if you haven’t received your charge card, contact your employer or call our Customer Support Team on 016 88 16 00)
- The charge card is already activated for use at public charging stations
- You can activate your card for home use in just a couple of steps using the details below (see FAQs)
- How do I link the KBC Autolease charge card to my 50five charge point?
- How do I set up automatic reimbursement of my charging sessions at my 50five charge point?

- Download and open the 50five app
- .Tap ‘My charge point’ and tap it a second time or scroll down
- Select ‘Settings’
- Tap ‘Authorised charge cards’
- Tap the ‘+’ sign at the top right of your screen to add a new charge card
- Enter the charge card number (this number starts with BE and can be found on the back of your Network Fleet Card (= your KBC Autolease charge card))
7. Check whether the charge card appears correctly under ‘Authorised charge cards’
You can now charge your vehicle with your charge card at your 50five charge point. If your employer reimburses your home charging sessions, set up automatic reimbursement. Please note: After adding the charge card, it can take up to max. 15min before the option for automatic reimbursement appears.
If your KBC Autolease lease includes a charge point, charge point subscription and charge card, and if your employer reimburses home charging sessions, it is possible to set up automatic reimbursement. The standard reimbursement rate (in euros per kWh) is based on the regional CREG rate and is set by 50five.
Link your KBC Autolease charge card to your 50five charge point (see previous FAQ) and then activate automatic reimbursement:
- Open the 50five app
- Tap ‘My charge point’ and tap it a second time or scroll down
- Select ‘Settings’
- Tap ‘Automatic reimbursement’
- Tap the pencil icon at the top right of your screen
- . Set the toggle to on or off to activate or deactivate automatic reimbursement
- Click on 'Account' at the bottom
- . Click on 'Billing
- Click on 'Payment details
- Click on the pencil icon
- . Fill in your account number
- . Save your details.
In the app, you will find the reimbursement rate under 'My charge point' - Rate.
You can consult these charging sessions in your 50five account
- Go to https://50five-sbelux.evc-net.com
- Log in.
User name and password are the same as for the 50fiveapp. - Click on 'Transactions’
- Select 'Transactions at own charge point' under Show
- Click on the green 'Show' button
- You can print or export the results.
In your 50five account https:/50five-sbelux.evc-net.com/ you can
- track charging sessions at your own charge point (= transactions)
- consult and download reimbursement documents;
- consult the status of your charging station.
- find nearby charge points
- check the automatic reimbursement rate and the guest rate
- check the status of the charge card
- get support (FAQs, chat with the AI Agent, contact form for questions, comments or complaints, follow up your tickets)
Please state explicitly in your application whether you want to use this charge card exclusively at your 50five charging station or also at public charging stations.
In the Shell app, you will find the charging history of all charging sessions with your KBC Autolease charge card.

You can also download the app by scanning this QR code.
You can also order a personal charge card in the Shell app and use it, for example, to charge up at fast-charging stations and when you’re abroad if your car policy does not permit such charging sessions.

You can also download the app by scanning this QR code.
Yes, they can.
- The guest rate is set to semi-public* by default
- As standard, the rate is set at the regional CREG rate + a roaming fee of 0.05 euros
- As the ‘owner’ of the charge point, you will be charged the CREG rate
- The guest rate can be switched on or off and the rate can be changed by submitting a ticket in the 50five app
* a semi-public charge point is not visible in apps
Yes, you can.
You are then treated as a guest user of your own 50five charge point. See the frequently asked question ‘Can my guests charge up at my charge point?’
Users of the electrical grid who have a charging station are required to register this with their distribution system operator. Those who fail to do so may face an administrative fine. Charging stations for electric vehicles must be registered in Flanders and Wallonia, but this is not yet required in Brussels.
This new requirement is intended to help predict the electricity needs of households and businesses, especially as the number of electric vehicles on Belgian roads is expected to increase. This information will allow grid operators to better anticipate changes on the distribution network and make targeted adjustments.
- In the Flemish Region, the Flemish Regulator for the Electricity and Gas Market (VREG) introduced the mandatory registration of charging stations for electric vehicles in June 2021.All charging stations connected to the low-voltage grid with a load capacity of 5 kVA or more must be registered with Fluvius.
- In the Walloon Region, the most recent electricity market decree came into force on 15 October 2022. This requires any grid user with a charging station to register this with the grid operator.
- In the Brussels-Capital Region, charging stations currently do not have to be registered, but this is likely to change in the near future.
- In the Flemish Region, you must register your charging station with Fluvius
- Go to Fluviuso
- Make sure you have the EAN code of your existing electricity connection to hand. Your EAN code can be found on the energy bills from your supplier.
- What should you enter in the following fields if you have a 50five charging station?
- Name of installer: 50five
- Type of charging system: Single charging station
- Access to charging system: Personal
- Does the system use smart charging? Yes, the charging station applies an agreed limit on peak consumption
- Charging station manufacturer: Peblar
- Name of charging station model (manufacturer): Home Plus
- Number of charging stations (= number of plugs/sockets): 1
- Maximum configured capacity per charging station: Single-phase: 7.4 kWThree-phase: 22 kW
- There are five distribution system operators in the Walloon Region: ORES, RESA, AIEG, AIESH en REW
- In the Brussels-Capital Region, Sibelga is the network operator but you are not currently required to register your charging station.
If you have any questions, contact your grid operator.
Your partner can charge with his/her charge card as a guest user at the guest rate. The guest tariff is on by default.
Yes, you can. Before installing a charge point for a flat, a specialist from 50five will always carry out an on-site inspection (this costs 202 euros excluding VAT).
It is the driver's responsibility to obtain the correct information and permissions from the property managing agent, home insurer and fire brigade before installing a charge point.
As a tenant, you do not have the right to have a charging station installed at your own initiative. Such decisions are up to the owner.
If you do have a charging station installed, it becomes the property of the owner of the house or apartment you’re renting, even if you paid for it.
If you cannot have a home charging station installed, you will have to charge your vehicle at public charging stations or at work.
- To charge your EV at public charging stations, you need a charge card, such as the NFC charge card, which you can use to charge your vehicle at more than 99% of public charging stations in Belgium.
- Your employer’s car policy should stipulate whether you can charge your vehicle at work.
Make sure to carefully plan your charging sessions at work or nearby, especially if you’re planning a longer drive.
Take the test with the ‘Guide to Driving Electric Vehicles’ (only in Dutch). In a few steps, you will find out whether electric driving is the right choice for you and which electric vehicle is the best fit for you.
We highly recommend informing your insurance agent if you’re having a charging station installed at your home.
They can then include it in your home insurance policy.
This may involve a slight increase in your insurance premium.
No, the charging station is not covered under your car insurance.Damage to your charging station due to an external cause is covered under your home insurance. Please contact your home insurer about this matter.
Contact your insurance agent for help with filing the claim.
Yes, if you prepare properly, you can drive long distances in an electric vehicle.
But don’t forget: if you take the motorway to your holiday destination in a fully loaded vehicle with two bicycles on a bike rack and the air conditioning set to 20°C, your vehicle’s electricity consumption will be considerably higher than normal. In other words, make sure you plan to recharge on time.
A few key tips
- Map out your route well in advance
- Install at least 2 route planner apps on your mobile phone such as ‘A Better Routeplanner’
- Download apps from major charging networks such as Ionity, Fastned, Tesla, etc.
- Make sure you are familiar with the built-in navigation system of your electric vehicle
- Plan when you’ll stop to charge and give yourself enough flexibility
- Keep an eye on your car's driving range when you’re on the road, or better still, let your fellow passenger do this
- While travelling, charge at fast-charging stations with a charging power of at least 50 kW
- Select fast-charging stations and minimum charging power in your charge card app
- Some fast-charging stations are also set at 100 kW or even 350 kW, so check the maximum charging power of your vehicle
- Remember that fast-charging stations only allow you to charge your battery up to 80%
- Carry at least 2 or 3 international charge cards, and make sure you have a physical version of them (i.e. not just the app)
- If you’re travelling and need to stay somewhere overnight, choose a hotel or B&B with the option to charge your vehicle there or at a fast-charging station nearby
- Don't travel during busy weekends as you’ll inevitably get caught in traffic jams and queues for fast-charging stations
- Bring two charging cables:
- A mode 3 charging cable for charging at public charging stations
- A mode 2 charging cable for charging from an ordinary socket (e.g., at your holiday home) in emergencies
- The charging cable at fast-charging stations along motorways is permanently connected to the station itself, so you don't need a separate cable to use it
- Drive at a constant speed of 110 km/h while on the motorway
- A Better Routeplanner
- PlugShare
- Fastned
- Ionity
- Tesla
- Sygic
- Shell Recharge
- ANWB
- Google Maps
Electric charge points in Belgium must be connected to a separate electrical circuit and protected by a suitable circuit breaker and switch. The certified installation partner of 50five will ensure that the installation meets all technical and legal requirements so that it may then undergo AREI inspection by an independent inspection body.
Your charge point should ideally be installed as close as possible to the electrical box in order to reduce the cost of installation and remain within the scope of the standard KBC Autolease installation package. During the video appointment with 50five, you will be informed about the best location and any additional (installation) costs.
- You don't need to provide any cabling yourself.
- The video appointment will include a discussion of what you should provide or prepare, if anything.
Plan when you’ll charge your vehicle or set charging schedules using your vehicle's app.
You will soon be able to use the 50five app to programme your charge point with charging schedules. You plug in the charging cable and activate the charging session when you park the vehicle, but the charging session will only start according to the programmed schedule.
50five's charge points are suitable for any type of connection to the grid. The video appointment will include a discussion of the optimal charging solution and you’ll receive clear advice.
Statistically, electric vehicles are much less likely to catch fire than vehicles with an internal combustion engine. We highly recommend informing your insurance agent if you’re having a charge point installed at your home.
The 50five charge point can be combined with local energy storage such as a home battery. However, an Energy Management System to control the charge point and home battery is not offered by KBC Autolease or 50five.
If you charge your electric vehicle while the solar panels are producing electricity, this will be used to power any devices (such as your vehicle) consuming electricity at that time. If the solar panels produce insufficient power to meet the amount required, it will be supplemented with electricity from the grid.
Please note that the 50five charge point does not include an Energy Management System to optimise the charging process involving solar panels or a home battery.
An Energy Management System (EMS) is a powerful tool to manage, control and optimise energy consumption.
While an EMS can control the charge point in principle, 50five and KBC Autolease do not offer this type of system. The driver is wholly responsible for the installation of an EMS and its use in combination with a charge point from 50five.
It is generally believed that a charge point should easily last eight to 10 years, which is equivalent to twice the lifetime a company car. Depending on technological advancements (such as vehicle-to-grid applications), it may be preferable to replace the charge point sooner.
A supplier warranty applies to the charge point for the duration of the lease (up to a maximum of five years). The conditions for transfer of ownership if you move house or leave the company should be stipulated in your employer’s car policy.
After installing the charge point, the installation technician will connect it to the Internet by following the steps below:
- 4G connection using a SIM card in the charge point
The charge point is equipped with a 4G SIM card to connect to the back office of 50five over the Internet. - Ethernet cable
The charge point is connected to the modem using an Ethernet cable. If there is no modem nearby, a UTP cable will be connected and a mobile router installed. - Wi-Fi In exceptional cases, the charge point is brought online via a Wi-Fi connection. This means that the charge point has to be near the Wi-Fi router transmitting the signal.
You can reset your charge point by using the 50five portal.
- Log in to your account at https://50five-sbelux.evc-net.com/
- Open the ‘Charge points’ menu
- On the left-hand side of the table, select the ID number of the charge point to be reset
- Choose ‘Soft reset’ to restart the software5. Choose ‘Hard reset’ to restart the hardware
